Introduction
Hey guys! I've been using React for a while now, and I thought, "Why not share what I've learned?" Exciting, right? So In today’s article, we'll dive into the basics of React. We'll explore its core concepts and benefits. if you just starting out, understanding React’s component-based architecture revolutionize your approach to web development.
Prerequisites
Before diving into React, it's essential to have a solid understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Familiarity with ES6 features, such as arrow functions, classes, and modules, is advantageous. Additionally, a grasp of the Document Object Model (DOM) and how it interacts with JavaScript will facilitate a smoother learning curve but we are still going to talk about it in this article too. Let’s dive right in 😉
What is React?
React is an open-source JavaScript library created and maintained by Facebook. It is specifically designed to make building user interfaces for websites or web applications easier and more efficient. So, instead of starting from scratch every time you want to create a part of a website that changes based on user interactions or updates, you can use React's tools to build these parts quickly and effectively.
All that we just talked about can be achieved by using a concept in React called "components." Components are like building blocks you can assemble to create your web interface. Each component represents a specific part of your page, like a button, a form, a header, or a whole section. So, you can combine these components to build complex user interfaces.
One of the challenges I faced while learning React was not conducting thorough research beforehand. I chose to learn it primarily due to its popularity and widespread use in many tech companies, without pausing to ask myself a crucial question: 'Why should I learn or use React?’
So here are the reasons you should consider using React.
Why Would You Use React?
There are many reasons you should consider using React, but we are going to be looking at a few of them that are important.
Efficient UI Development: React's component-based architecture allows you to create reusable and modular UI components(such as cards, buttons, and forms). This makes it much easier to manage your code, build complex interfaces, and maintain your project over time. We can use LEGO bricks as a perfect analogy for better understanding.
React helps you build web pages like using LEGO bricks. Each brick is a "component" that does a specific job, like making a button, showing a picture, or arranging things neatly. You can use these components over and over to create your web page.
Reusability: React promotes component reusability, which means you can create components once and reuse them across your application or even in different projects. This saves you time and effort in development and maintenance.
Virtual DOM: React uses a Virtual DOM, which is a lightweight representation of the actual DOM (Document Object Model).
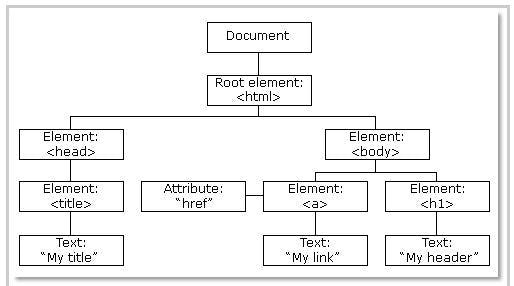
💡 The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming concept that represents a web page as a structured tree of objects. Each object corresponds to a part of the web page, such as elements like body title, or head.
When your data changes, React efficiently updates the Virtual DOM which simply means that React updates parts of the web page that needs to be updated without reloading the entire page which will improve performance and reduce the number of direct DOM manipulations, leading to faster and smoother user experiences.
JSX (JavaScript XML): JSX is a syntax extension that allows you to write HTML-like code within your JavaScript. It combines the power of JavaScript with the familiarity of HTML, making it more intuitive to describe UI components and their structure. So for example, Let's say you want to display a variable value inside a paragraph tag. Here is how it will look in JSX 👇🏽
//App.jsx import React from 'react'; function App() { const message = 'Hello, React!'; return ( <div> <p>{message}</p> </div> ); } export default App;In this example, JSX allows you to directly embed the JavaScript variable
messagewithin the<p>tag using curly braces{}. React will replace the{message}with the value of themessagevariable, resulting in the text "Hello, React!" being displayed on the webpage. This way, you're blending regular HTML with dynamic JavaScript values seamlessly using JSX within your React component. Also, the extension to save a jsx file is.jsx💡 Just focus on the JSX part of the code we just looked at. We’ll discuss more of what is going on later in this series.
Declarative Syntax: React uses a declarative approach to building UIs. You describe what you want your UI to look like based on your application's state, and React takes care of updating the UI to match that description. This makes your code more predictable and easier to reason about.
Job Opportunities: React is widely used/adopted in the industry, so learning it can open up many job opportunities for frontend and full-stack developers.
Basic Architecture of how React works?
Here is a diagram I came up with to illustrate how react works.
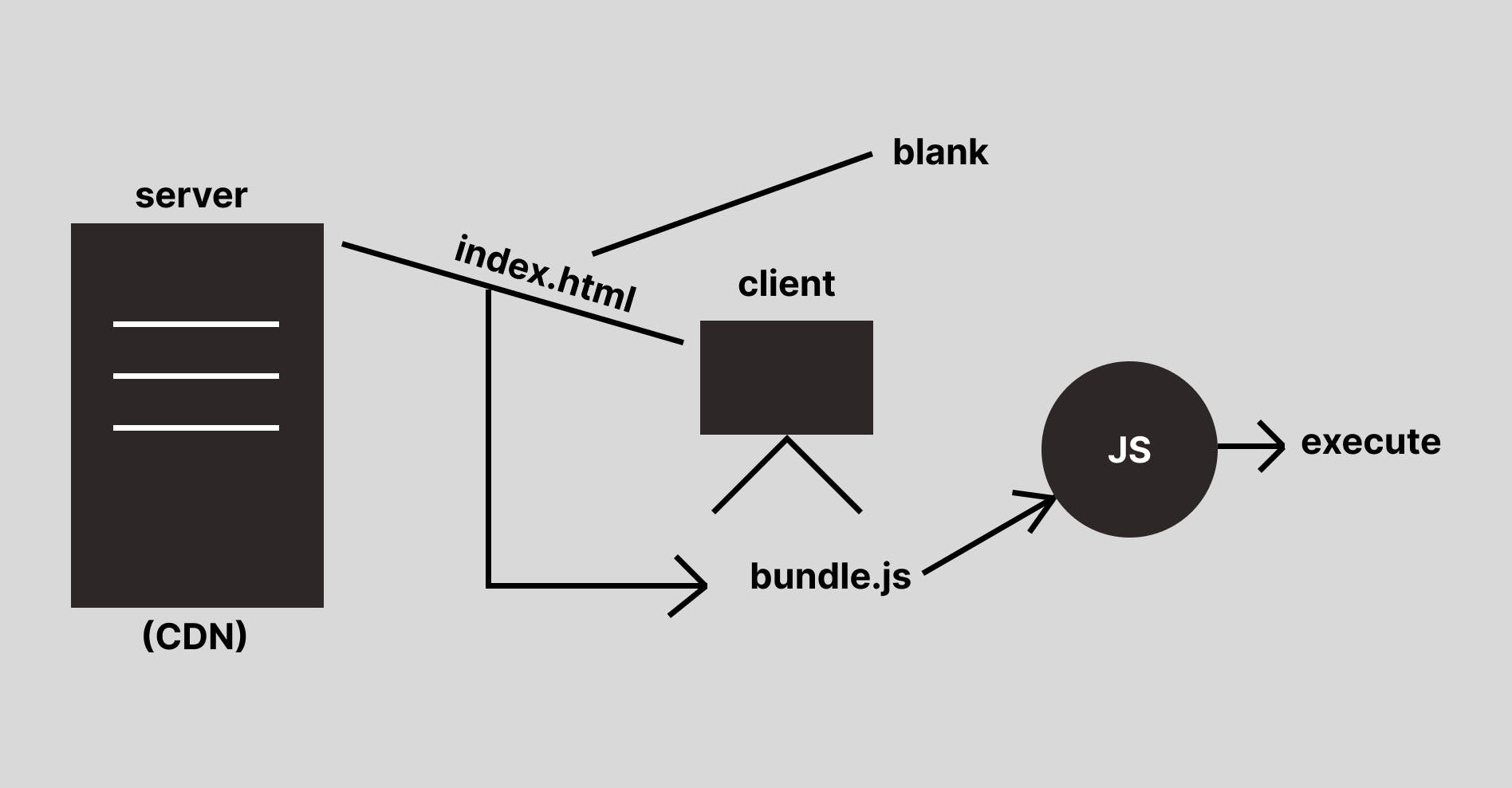
The way React operates involves both the Server and the Client. In this scenario, the Server can take the form of a CDN(Content Delivery Network), which serves files like an HTML document but doesn't handle computations. During communication, the CDN provides an index.html file to the Client.
Inside this index.html, there's a React file – often called bundle.js or with any preferred name – which is, in fact, a collection of JavaScript codes. However, the index.html itself appears blank; its purpose is to deliver the JavaScript file to the Client.
When this JavaScript bundle (bundle.js) is sent to the Client, it's executed by the Client's browser. This initial execution helps the Client understand how the page should look and behave. As a result, React works to manage the virtual representation of components in the browser's memory, updating the actual DOM efficiently to create a dynamic and responsive user interface. I really hope that made sense!
Conclusion
That’s all guys and congrats on getting to the end of this article 🎉 🎉. Don’t worry if everything does not click at first. As we go along in this series you’ll get a better understanding of how to use React and how it works. Have a nice weekend and see you next week 😀
